Tooth decay is one of the most common issues in our society, and modern dentistry has made a lot of strides to battle against this. Dentists are now moving towards an approach to this, including management that’s tailored to personal risk rather than just a singular size fits every case, which it doesn’t.
In the past, drilling and filling was the only way, but this didn’t change the conditions of this, and it could lead to more risk for infection and disease, and it doesn’t fully fix the issue. But, buy profiling the degree of risk, and creating a more individualized preventative strategy, today’s’ dental professionals are using an approach that really works.
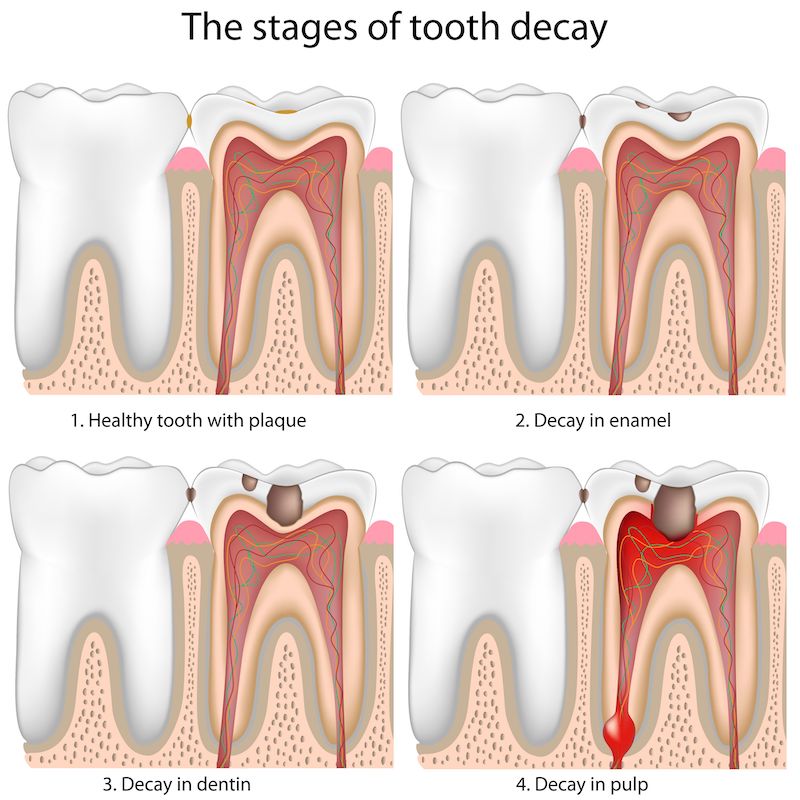
Dental decay is a dynamic and infectious disease process. The mouth is more of an ecosystem than anything else, which means that the living organism is continually interacting with every other element within the environment.
The teeth are made up of an outer covering of enamel, a mineralized structure made of calcium and phosphate. The minerals are oftentimes bathed in a fluid, and ideally, you want a neutral environment that’s a balance between this. Acidity is measured on a pH scale, and if you have a low pH that means it’s acidic. If it’s around 7, that’s neutral. The thing is, the reason why your mouth is so acidic is, of course, the bacteria. They create plaque, which is a whitish sand sticky biofilm that collects and forms on the mouth.
Every time you sugars and carbs, his will cause it to break down, creating a byproduct, which also makes the mouth much more acid. When your pH is around 5.5, the minerals are usually dissolved below the surface. During his, more and more of the calcium and phosphate leave, which then softens this, and usually, the roots and dentin are exposed. It’s susceptible to decay, and he roots will de-mineralize quickly and easily when you have a more neural saliva pH.
What can you do about this then?
Well, you may want to fires and foremost look into the risk that you have in terms of tooth decay. For the most part, a risk assessment will help you look at the disease-causing aspects of it, and the health-promoting factors that go with this too. Usually, each person has a unique balance that’s changing constantly, and the challenge is to identify what’s out of balance and also improve protection and health.

Usually, the caries risk assessment will be linked to heart disease, and most of the time, a physician will look at your health history, take your blood pressure, monitor your heart, and give you a treatment plan in order to manage the risk. If your blood pressure is high, it usually means you’re at a risk. Dentists will use this in a similar fashion to measure the [pH of your mouth, so you can figure out what you’re at risk for.
The thing is, everyone’s mouth is different. Even if you eat the same things as another person, the risk is much different, and it’s predisposed in most cases to different genetic risks and factors. With that being said, you should talk to your doctor about the risks of this, and consult your dentist in Rapid City to help you figure out what’s going on. with a more individualized plan on hand, you’ll be able to, with this as well, improve on your own personal health and wellness. Plaque and caries are all different in everyone, based on their own needs, so make sure you learn about what your mouth is like and work to reduce the acids within the mouth, so the breakdown can cease.